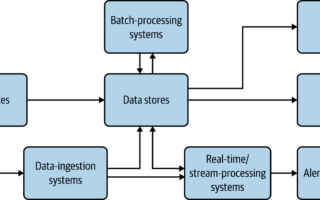
In the digital age, the ability for systems, applications, and software to communicate seamlessly is not just an advantage but a necessity. This is where the concept of Integration Architecture comes into play, serving as the silent orchestrator behind the scenes, ensuring that diverse systems work together in harmony. This comprehensive exploration delves into the essence of Integration Architecture, its components, significance, and the transformative impact it has on businesses and user experiences.
The Essence of Integration Architecture
Integration Architecture is a strategic framework within the realm of information technology, designed to facilitate the seamless interaction between disparate systems, applications, and software within an enterprise. It aims to create a unified environment where data and processes can flow freely across different platforms, regardless of their underlying technologies or architectures. This interconnectedness is crucial for businesses to operate efficiently, innovate, and provide superior services to their customers.
Key Components
- Integration Patterns: These are standardized methods or solutions for addressing specific integration challenges, such as data synchronization, process orchestration, and service composition.
- Middleware Technologies: Acting as the glue between different systems, middleware technologies, including message brokers, API gateways, and Enterprise Service Buses (ESBs), provide the necessary infrastructure for enabling communication and data exchange.
- APIs (Application Programming Interfaces): APIs play a pivotal role in integration architecture, allowing different systems to communicate by defining a set of rules and protocols for interaction.
The Significance of Integration Architecture
In an era dominated by digital transformation, the role of Integration Architecture cannot be overstated. It serves as the foundation for creating agile, scalable, and efficient IT ecosystems that can adapt to changing business needs and technological advancements.
Enhancing Business Efficiency
By automating the data exchange between systems and streamlining processes, Integration Architecture significantly reduces manual effort, minimizes errors, and accelerates business operations. This leads to improved productivity and operational efficiency.
Facilitating Innovation and Agility
With a robust integration framework, businesses can more easily adopt new technologies, enter new markets, and respond to competitive pressures. Integration Architecture enables organizations to leverage the best-of-breed solutions without being constrained by compatibility issues.
Improving User Experience
Seamless integration ensures that users have a cohesive and intuitive experience across various applications and services. This integration is particularly important in customer-facing applications where a disjointed user experience can lead to dissatisfaction and churn.
The Evolution of Integration Architecture
The concept of Integration Architecture has evolved significantly over the years, from simple point-to-point connections to complex, cloud-based ecosystems.
From Point-to-Point to Service-Oriented Architectures
Initially, integration efforts were often limited to point-to-point connections, leading to a tangled web of connections that were difficult to manage. The adoption of Service-Oriented Architectures (SOAs) marked a shift towards more modular and reusable services, simplifying the integration landscape.
The Rise of Microservices and Cloud Integration
The microservices architecture has further advanced the principles of SOA, breaking down applications into smaller, independently deployable services. Coupled with cloud integration platforms (iPaaS), businesses can now achieve unprecedented levels of flexibility and scalability in their integration strategies.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its benefits, implementing an effective Integration Architecture is not without challenges. It requires a careful balance of technical, strategic, and organizational considerations.
Ensuring Scalability and Flexibility
As businesses grow and evolve, their integration architecture must be able to scale accordingly. This requires forward-thinking design principles that accommodate future technologies and changing business requirements.
Navigating the Technology Landscape
The rapid pace of technological change presents a constant challenge. Integration architects must stay abreast of the latest trends and technologies, from AI and IoT to blockchain, to ensure their integration strategies remain relevant and effective.
Security and Compliance
Integrating different systems invariably raises concerns about data security and regulatory compliance. Robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and audit trails, must be integral components of any integration architecture.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Integration Architecture
As we look to the future, Integration Architecture is set to play an even more critical role in the digital landscape. The proliferation of IoT devices, the increasing reliance on big data and analytics, and the ongoing shift towards cloud-native applications are just a few of the trends that will shape the evolution of integration strategies.
Embracing AI and Automation
Artificial Intelligence and automation technologies offer new opportunities for enhancing integration architectures, from intelligent routing and error handling to predictive analytics and proactive maintenance.
The Convergence of Integration and DevOps
The principles of DevOps, emphasizing continuous integration, delivery, and deployment, are increasingly being applied to integration architecture. This convergence aims to further streamline processes, reduce time-to-market, and enhance collaboration across development and operations teams.
Sustainable and Ethical Integration
As societal awareness of environmental and ethical issues grows, businesses are under pressure to ensure their operations, including their IT practices, are sustainable and ethically sound.