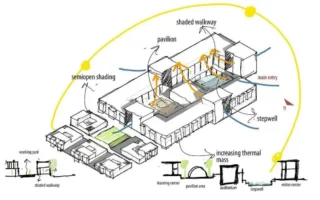
Introduction:
In the realm of architecture, creativity often takes the spotlight, with visions of stunning buildings and innovative designs captivating our imagination. Yet, beneath the surface of aesthetics lies a foundation deeply rooted in science, particularly physics. In this article, we delve into the relationship between physics and architecture, exploring why an understanding of physics is essential for architects and how it influences every aspect of architectural design.
1.Understanding the Basics: What is Architecture?
Defining Architecture: Beyond mere buildings, architecture encompasses the art and science of designing spaces that serve both functional and aesthetic purposes.
The Role of Architects: Architects are not just designers; they are problem-solvers who must consider numerous factors, including site conditions, building materials, structural integrity, and environmental sustainability.
2.The Physics Behind Architecture: Why It Matters
Structural Integrity: Physics plays a crucial role in ensuring that buildings can withstand various forces, such as gravity, wind, and seismic activity.
Load-Bearing Principles: Architects must understand concepts like compression, tension, and shear to design structures that can support their own weight and the loads they will bear over time.
Material Properties: From concrete and steel to glass and wood, each building material has unique physical properties that influence its suitability for different architectural applications.
3.The Influence of Physics on Architectural Design:
Form and Function: Physics influences the shape and layout of buildings, dictating everything from the angle of a roof to the size of windows for optimal daylighting.
Energy Efficiency: Concepts like thermal insulation and passive solar design leverage physics principles to reduce energy consumption and create more sustainable buildings.
Acoustics and Sound Control: Understanding the behavior of sound waves is essential for designing spaces with optimal acoustics, whether it’s a concert hall or an office building.
4.Tools and Technologies: Applying Physics in Architecture
Computer-Aided Design (CAD): Architects use software tools that simulate physics principles to model and analyze structural performance, airflow, and lighting conditions.
Building Information Modeling (BIM): BIM platforms integrate physics-based simulations with architectural design, enabling architects to explore various scenarios and optimize their designs for efficiency and performance.
5.Case Studies: Real-World Examples
The Sydney Opera House: Renowned for its iconic design, the Sydney Opera House required precise engineering to realize its distinctive shell structures, which were inspired by natural forms like the segments of an orange.
The Burj Khalifa: As the tallest building in the world, the Burj Khalifa in Dubai exemplifies how physics principles are applied to overcome challenges such as wind loads and vertical transportation in supertall structures.
6.Education and Training: Bridging the Gap
Integrating Physics into Architectural Curricula: Many architecture programs include coursework in structural engineering, environmental science, and building physics to equip students with the knowledge they need to succeed.
Lifelong Learning: In a rapidly evolving field, architects must stay abreast of advancements in materials, construction techniques, and sustainability practices, often through continuing education and professional development opportunities.
Conclusion:
In the dynamic world of architecture, the marriage of art and science is evident at every turn. While creativity fuels the vision, physics provides the framework upon which architectural masterpieces are built. From the soaring heights of skyscrapers to the intimate spaces of homes, the principles of physics shape our built environment, reminding us that in architecture, form truly follows function. So, to answer the question, “Do you need physics for architecture?”—the resounding answer is yes, for without it, the very foundations of our structures would crumble.