Introduction:
Architecture serves as a tangible expression of culture, history, and human ingenuity. Among the myriad styles that have graced the built landscape over the centuries, Gothic and Romanesque stand out as two distinct but interconnected chapters in architectural history. In this exploration, we delve into the major differences between Gothic and Romanesque architecture, uncovering the unique characteristics and underlying philosophies that distinguish these iconic styles.
1.Origins and Historical Context:
Romanesque Architecture: An Expression of Early Medieval Power and Piety
Gothic Architecture: A Testament to the Triumph of Light and Faith over Darkness
2.Structural Elements:
Romanesque Architecture: Solidity and Symmetry in Stone
Thick Walls and Rounded Arches: Symbolizing Strength and Stability
Barrel Vaults and Groin Vaults: Distributing Weight and Supporting Massive Structures
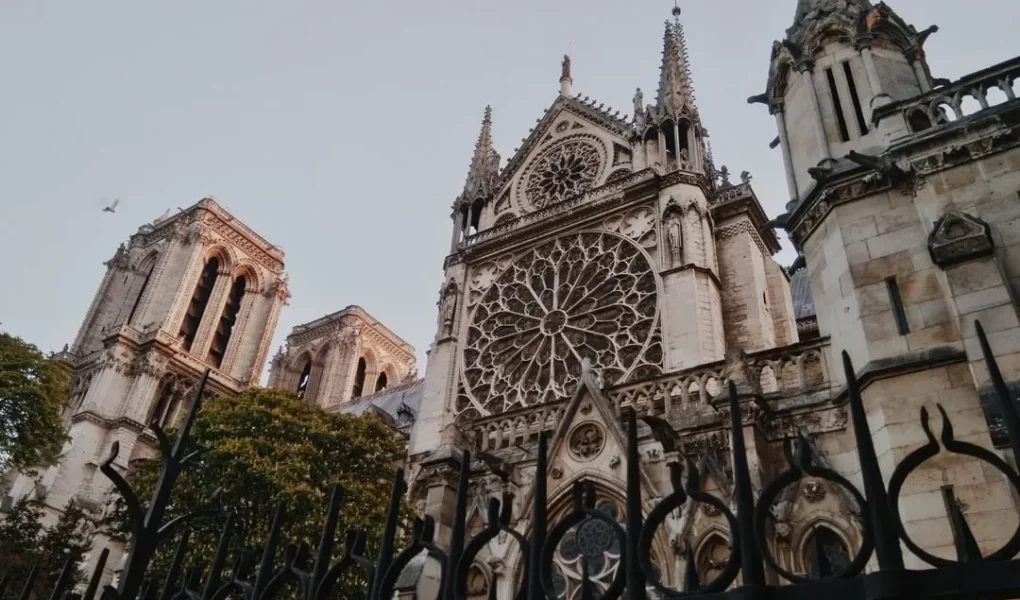
Gothic Architecture: Ethereal Heights and Graceful Forms
Pointed Arches and Ribbed Vaults: Channeling Weight Vertically and Allowing for Greater Height
Flying Buttresses: External Supports Embracing Lightness and Innovation
3.Aesthetic Characteristics:
Romanesque Architecture: Ornate Simplicity and Earthly Grandeur
Decorative Capitals and Sculptural Reliefs: Depicting Biblical Narratives and Symbolism
Small Windows and Dim Interiors: Creating an Atmosphere of Mystique and Contemplation
Gothic Architecture: Elegance in Motion and Divine Aspiration
Elaborate Tracery and Stained Glass: Infusing Spaces with Color and Luminescence
Tall, Narrow Windows and Light-Filled Naves: Inviting Worshipers to Gaze Heavenward in Awe
4.Religious Symbolism and Function:
Romanesque Architecture: Fortress of Faith and Refuge of the Divine
Monolithic Churches and Monasteries: Centers of Spiritual Authority and Community Life
Cloisters and Crypts: Sanctuaries for Prayer, Reflection, and Burial
Gothic Architecture: Cathedrals of Transcendence and Spiritual Aspiration
Cathedral Complexes and Pilgrimage Routes: Drawing the Faithful and the Curious Alike
Choirs and Ambulatories: Facilitating Rituals and Processions, Leading Worshipers on a Journey of Salvation
5.Evolution and Influence:
Romanesque Architecture: Laying the Foundation for Gothic Innovation
Transition from Roman to Gothic: Experimentation with Height and Light
Regional Variations and Hybrid Styles: Reflecting Cultural Exchange and Artistic Synthesis
Gothic Architecture: Pushing the Boundaries of Human Achievement and Divine Revelation
High Gothic and Flamboyant Gothic: Culminating in Masterpieces of Engineering and Artistry
Renaissance and Beyond: Inspiring Revivals and Resurgences, Leaving an Indelible Mark on Architectural History
Conclusion:
In the tapestry of architectural evolution, Gothic and Romanesque styles stand as timeless testaments to human creativity, spirituality, and aspiration. While Romanesque architecture embodies the solidity and symmetry of earthly power and piety, Gothic architecture transcends earthly bounds, reaching skyward in a quest for divine light and grace. By understanding the major differences between these two iconic styles, we gain deeper insight into the rich tapestry of architectural history and the enduring legacy of human ingenuity.