Introduction:
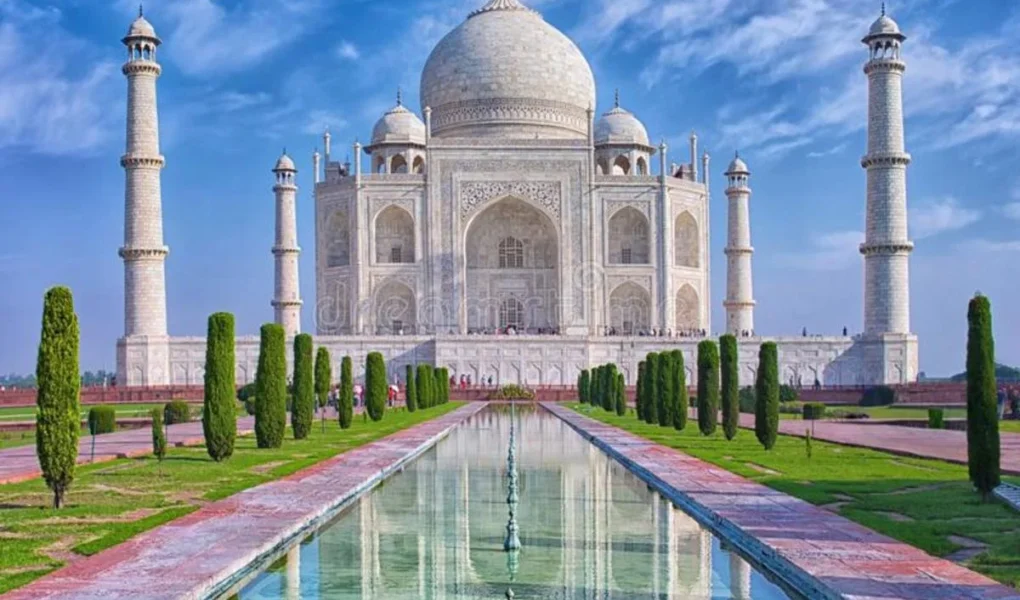
Mughal architecture stands as a testament to the grandeur and sophistication of the Mughal Empire, with the Taj Mahal emerging as an unparalleled masterpiece. Commissioned by Emperor Shah Jahan in memory of his beloved wife Mumtaz Mahal, this architectural marvel represents the pinnacle of Mughal achievement. In this exploration, we delve into the splendor of the Taj Mahal, unraveling its intricate design elements and enduring significance.
1: Historical Context
The Mughal Dynasty: A Golden Era of Indian Architecture
Shah Jahan’s Reign: Patronage of the Arts and Architecture
The Love Story Behind the Taj Mahal: Mumtaz Mahal’s Enduring Legacy
2: Architectural Features
Symmetry and Balance: The Perfect Harmony of Design
The White Marble Wonder: Materials and Construction Techniques
Calligraphy and Ornamentation: Intricate Details That Tell a Story
3: Structural Marvels
The Central Mausoleum: Symbolism and Spiritual Significance
The Four Minarets: Guardians of the Taj Mahal
The Reflecting Pool: Creating Ethereal Beauty Through Water
4: Cultural Significance
UNESCO World Heritage Site: Recognizing Cultural Heritage
Symbol of Love: Inspiring Romance and Admiration
Religious Syncretism: Blending Islamic, Persian, and Indian Influences
5: Artistic Influences
Persian Inspiration: Tracing Roots in Safavid Architecture
Indian Innovations: Incorporating Local Techniques and Traditions
European Exchange: Global Influences on Mughal Aesthetics
6: Preservation Efforts
Conservation Challenges: Protecting the Taj Mahal from Environmental and Human Impact
Restoration Projects: Safeguarding the Legacy for Future Generations
Sustainable Tourism: Balancing Preservation with Accessibility
7: Cultural Impact
Icon of India: A National Treasure and Source of Pride
Literary and Artistic Reverence: Inspiring Poetry, Paintings, and Prose
Tourism and Economy: Driving Local Development and International Interest
8: Controversies and Debates
Ownership Disputes: Legal Battles Over Heritage Rights
Environmental Concerns: Pollution Threats to the Taj Mahal’s White Marble
Political Symbolism: Appropriation and Manipulation of Historical Narratives
9: Future Prospects
Digital Preservation: Harnessing Technology to Document and Protect the Taj Mahal
Educational Initiatives: Promoting Awareness and Appreciation of Mughal Architecture
Sustainable Development: Balancing Tourism and Conservation Efforts
Conclusion:
The Taj Mahal stands as a timeless testament to the vision and skill of Mughal architects and artisans, capturing the essence of beauty, love, and devotion. As a high point of achievement in Mughal architecture, it continues to inspire wonder and admiration, transcending time and borders. Through preservation efforts and cultural initiatives, we ensure that this architectural jewel remains a symbol of human creativity and ingenuity for generations to come.