Introduction:
In the realm of gastroenterology, the term “intact villous architecture” holds paramount importance. It serves as a cornerstone in understanding the functionality of the gastrointestinal tract and plays a pivotal role in diagnosing various gastrointestinal disorders. But what exactly does intact villous architecture entail? This comprehensive guide aims to unravel the intricacies of intact villous architecture, elucidating its significance, structure, and implications in gastrointestinal health.
Understanding Villi and Intact Villous Architecture
1.Anatomy of the Small Intestine
The small intestine, a crucial component of the gastrointestinal tract, facilitates nutrient absorption.
Its inner lining is adorned with finger-like projections known as villi, which amplify its surface area.
2.The Role of Villi in Nutrient Absorption
Villi harbor specialized cells responsible for nutrient absorption, including carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
This absorption is pivotal for sustaining bodily functions and overall health.
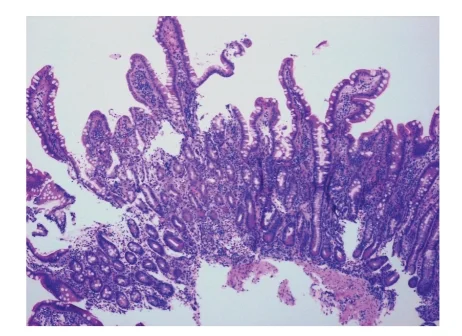
3.Defining Intact Villous Architecture
Intact villous architecture refers to the undamaged, healthy structure of these villi.
It implies that the villi are elongated, uniform in shape, and properly distributed across the intestinal lining.
The Significance of Intact Villous Architecture
1.Optimal Nutrient Absorption
Intact villous architecture ensures efficient nutrient absorption by maximizing the surface area available for absorption.
Any compromise in this architecture can lead to malabsorption syndromes, depriving the body of essential nutrients.
2.Barrier Function
Villi, when intact, act as a barrier against harmful pathogens and toxins, preventing them from infiltrating the bloodstream.
Disruption in villous architecture compromises this barrier function, predisposing individuals to infections and inflammatory conditions.
3.Diagnostic Importance
Assessment of villous architecture is integral in diagnosing gastrointestinal disorders such as celiac disease and tropical sprue.
Histological examination of intestinal biopsies helps clinicians evaluate the integrity of villous architecture, aiding in accurate diagnosis and management.
Clinical Implications and Disorders Associated with Altered Villous Architecture
1.Celiac Disease
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder characterized by the body’s immune response to gluten, leading to villous atrophy.
Damage to villous architecture in celiac disease results in malabsorption and various gastrointestinal symptoms.
2.Tropical Sprue
Tropical sprue is a gastrointestinal disorder prevalent in tropical regions, characterized by villous atrophy and malabsorption.
The exact etiology of tropical sprue remains elusive, but it is associated with bacterial or parasitic infections.
3.Refractory Celiac Disease
In some cases, individuals with celiac disease may develop refractory celiac disease, wherein villous atrophy persists despite adherence to a gluten-free diet.
This condition poses significant challenges in management and necessitates close monitoring to prevent complications.
Diagnostic Modalities for Assessing Villous Architecture
1.Histological Examination
Intestinal biopsies remain the gold standard for assessing villous architecture.
Histopathological analysis enables the evaluation of villous height, crypt depth, and the presence of inflammatory changes.
2.Endoscopic Techniques
Advanced endoscopic modalities such as confocal laser endomicroscopy (CLE) allow real-time visualization of mucosal architecture, aiding in the assessment of villous integrity.
3.Serological Markers
Serological tests, including anti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies and anti-endomysial antibodies, serve as screening tools for celiac disease but do not directly assess villous architecture.
Management Strategies for Disorders Affecting Villous Architecture
1.Dietary Modifications
In celiac disease and gluten-related disorders, adherence to a strict gluten-free diet is paramount in restoring villous architecture and preventing complications.
2.Pharmacological Interventions
Pharmacological agents such as immunosuppressants may be employed in refractory celiac disease to mitigate inflammation and promote mucosal healing.
3.Nutritional Support
Nutritional supplementation may be necessary in individuals with malabsorption syndromes to address deficiencies and promote optimal healing of the intestinal mucosa.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, intact villous architecture stands as a fundamental aspect of gastrointestinal health, facilitating nutrient absorption and maintaining barrier function. Understanding its significance and the disorders associated with its alteration is crucial in the diagnosis and management of gastrointestinal conditions. By harnessing diagnostic modalities and implementing tailored management strategies, healthcare professionals can strive towards preserving villous integrity and promoting optimal gastrointestinal function.